Vă întrebaţi poate ce face un calculator personal (PC). Ei bine, multe. Poate înlocui agenda personală, caietul cu adrese, cartea de telefoane, calendarul, caietul de notiţe, hârtiile, dosarele, bibliorafturile etc. Puteţi folosi computerul personal ca să vă uitaţi la TV sau să vedeţi filme pe DVD, puteţi asculta muzică sau emisiuni la radio, puteţi aranja fotografii în albume virtuale, puteţi transmite şi primi corespondenţă electronică şi puteţi chiar să sunaţi prietenii oriunde în lume. Înainte de a vedea cum, să comparăm diferitele părţi ale unui computer personal cu echipamentele din viaţa reală existente într-un birou.
You ask yourself what can a personal computer do for you. Well, it does a lot. It can replace the daily planner, address book, phone book, calendar, notepad, files, folders, papers and more. You can use your PC to watch TV and DVDs, listen to music or the radio, organize your photographs in virtual albums, send mail and even call long distance your friends. Before we do that, let's compare the different parts of a personal computer to their real-life counterparts found in most offices.
CPU (Unitatea centrală de procesare) = CREIERUL
CPU (Central Processing Unit) = THE BRAIN
 =
= 
Unitatea centrală de procesare (CPU) reprezintă creierul calculatorului. Nu este la fel de rapid sau de puternic precum creierul uman, dar face lucruri pe care creierul uman nu le poate face. Procesează pe nerăsuflate milioane de instrucţiuni pe secundă, în mod constant şi corect şi îşi aduce aminte de rezultate. În acest sens, computerul este un fel de maşină prostuţă. Procesează toate aceste informaţii, însă nu are habar ce înseamnă toate aceste informaţii. Cum arată acest tip de “creier” vedeţi mai jos. Cei doi mari producători de CPUs sunt Intel şi Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). Ambii producători fac circuite integrate (cipuri) excelente şi performante. Majoritatea computerelor din zilele noastre sunt echipate cu dual core CPUs. Un procesor dual core CPU se referă la acel CPU care include două procesoare complete într-un singur circuit integrat (cip). Procesoarele dual core reprezintă de fapt două “creiere” complete, în loc de unul singur. Gândesc mai bine două capete în loc de unul? În cazul de faţă, categoric da. În special pentru cei care lucrează mult cu aplicaţii video sau cu jocuri pe calculator. Aveţi nevoie de un dual core CPU ca să lucraţi la calculator? Nu, probabil că nu aveţi nevoie. Totul depinde de ce faceţi şi la ce folosiţi calculatorul.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the computer's brain. It is not as fast or as powerful as the human brain but it does something that the human brain cannot do. It blindly processes millions of instructions per second consistently and correctly and remembers the results. In this respect, the computer is a rather dumb machine. It processes all of this information but has no idea what it all means. You have below some examples of such a “brain”. The two major manufacturers of CPUs are Intel and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). Both make excellent integrated circuits (chips) and feature outstanding performance. Many computers today are coming equipped with dual core CPUs. A dual core CPU refers to a CPU that includes two complete processors in a single integrated circuit (chip). Dual core processors are well-suited for multitasking environments because there are two complete execution cores (brains) instead of one. Are two heads better than one? In this case, absolutely. Especially if you're doing extensive video work or playing demanding games. Do you really need a dual core CPU to perform the majority of PC tasks? No, probably not. It all depends on what you use your computer for.




RAM (Memoria) = BIROUL
RAM (Random Access Memory) = DESK
 =
= 
Memoria (RAM) se referă la stocarea de date care pot fi accesate în orice ordine sau la întâmplare. RAM într-un computer înseamnă memoria principală sau spaţiul de lucru şi este folosită pentru afişarea datelor şi pentru lucrul cu baza de date… ca un fel de birou. Acest tip de memorie arată ca nişte benzi şi au dimensiunea unor lame de gumă de mestecat. Majoritatea calculatoarelor personale au sloturi pentru adăugarea sau pentru înlocuirea memoriilor (RAM). Memoriile (RAM) pot fi pentru citire sau pentru scriere. Memoria (RAM) este ştearsă când se închide computerul, similar cu ordinea de pe biroul personal.
De ce memorie RAM aveţi nevoie? După CPU, RAM este cel mai important factor pentru performanţa calculatorului. Dacă aveţi un sistem de operare Windows XP, Microsoft recomandă un minim de 128MB (megabytes). Nu este tocmai suficient pentru Windows XP. Pentru o performanţă optimă cu aplicaţii standard desktop, se recomandă 512MB. Dacă aveţi un sistem de operare Windows 95/98 (ceea ce nu recomand) vă descurcaţi cu un minim de 128MB. Subliniez din nou, pentru cei care lucrează cu aplicaţii video sau cu jocuri pe calculator, memoria (RAM) necesară normală este 1-2GB (gigabytes).
Random Access Memory (RAM) refers to data storage that can be accessed in any order or randomly. RAM in a computer is considered main memory or the working area used for displaying and working with data...sort of like your desk. You open up all of your files, papers, reports, etc. and place them on your desk to work on. RAM performs the same function. This type of memory comes in sticks and are about the size of a few sticks of gum. Most PCs have slots for adding and replacing RAM. RAM can be both written to and read from. RAM is erased when a computer is shut down effectively clearing your desk.
How much RAM do you need? Next to the CPU, RAM is the most important factor in computer performance. If you are running Windows XP, Microsoft recommends 128MB (megabytes) as the minimum RAM requirement. This is not really an adequate amount for Windows XP. For optimal performance with standard desktop applications, 512MB is recommended. If you are running Windows 95/98 (and you shouldn't be), you need a bare minimum of 128MB. Again, video-intensive work or gaming requires more than normal amounts of RAM perhaps 1-2GB (gigabytes).
CE ÎNSEAMNĂ BYTE?
WHAT DOES ALL THIS BYTE STUFF MEAN?
-
Cea mai mică unitate de stocare memorie se numeşlte BIT. Un bit conţine fie UNU fie ZERO.
-
Opt bits reprezintă un BYTE. Destul spaţiu de stocare pentru o literă din alfabet.
-
1.024 bytes reprezintă un KILOBYTE (KB) sau aproximativ o pagină de text.
-
1.024 kilobytes reprezintă un MEGABYTE (MB) sau aproximativ 1.000 pagini de text.
-
1.024 megabytes reprezintă un GIGABYTE (GB) sau aproximativ 1.000.000 pagini de text.
-
The smallest unit of memory storage is called a BIT. A bit either contains a ONE or a ZERO.
-
Eight bits is one BYTE ("bite"). That's enough storage for about one letter of the alphabet.
-
1,024 bytes is one KILOBYTE (KB) or about one page of text.
-
1,024 kilobytes is one MEGABYTE (MB) or about 1,000 pages of text.
-
1,024 megabytes is one GIGABYTE (GB) or about 1,000,000 pages of text.
ALTE TIPURI DE MEMORII
OTHER TYPES OF MEMORIES
-
ROM înseamnă Read Only Memory. Această memorie păstrează toate instrucţiiunile de bază ale unui computer pentru sarcini simple, cum ar fi să facă să apară pe monitor litera “X” prin apăsare pe tasta “X”. Memoria nu poate fi schimbată, aşadar închiderea curentului nu afectează calculatorul.
-
CMOS înseamnă Complementary-symmetry/Metal-Oxide Semiconductor! Sună ciudat, nu-i aşa? Nu te obosi să memorezi. Stochează informaţia despre sistemul calculatorului precum şi data şi ora. Ca şi RAM, memoria are nevoie de curent ca să lucreze, însă consumul este infim. O baterie mică alimentează aceste informaţii şi ea ţine 4-5 ani. Dacă bateria CMOS s-a descărcat, calculatorul s-ar putea să nu ruleze corect. Trebuie să înlocuieşti neapărat bateria şi probabil să reintroduci informaţiile privind sistemul.
-
ROM stands for Read Only Memory. This memory holds all the basic instructions the computer needs to do very simple stuff, such as making the letter "X" appear on the monitor when you press the "X" key. This memory cannot be changed, so losing power does not affect it.
-
CMOS stands for Complementary-symmetry/Metal-Oxide Semiconductor! Sounds impressive, huh? Don't even try to remember that. It stores information about your computer system as well as the current date and time. Like RAM, this memory needs electricity to keep working, but it only needs a very small amount. A small battery will keep it running for 4-5 years. If the CMOS battery dies, your computer may not start up correctly. You will have to have the battery replaced, and, you will probably have to re-enter the setup information about your computer system.
HARD DRIVE = DULAPUL CU DOCUMENTE
HARD DRIVE = FILLING CABINET
 =
= 
Orice salvaţi pe calculator – documente, fotografii, filme, muzică, e-mail, programe şi altele – sunt compuse din una sau mai multe fişiere. Aceste fişiere, sunt întotdeauna grupate în dosare (folders) puse sub un director. Grupurile de dosare denumite sub-dosare (sub-folders) se regăsesc grupate întotdeauna sub un alt dosar (folder) – exact ca într-un dulap de documente. Acest aşa-numit “dulap” din computer se numeşte hard drive. Puteţi vedea cum sunt aşezate documentele pe hard drive în mai multe feluri. Prima metodă este să daţi click dreapta pe butonul START din stânga jos şi apoi click pe Explore.
Every item on your computer -- documents, photos, videos, music, email, programs, etc. -- is made up of one or more files. These files are always grouped in folders and make up your directory. Groups of folders, called sub-folders, are often filed together in another folder -- just like your filing cabinet. This "filing cabinet" on your computer is called a hard drive. You can see how this looks on your hard drive in several ways. One way is to use your mouse and right-click on the START button in the lower left corner of your screen and then left-click on "Explore".

Se deschide o fereastră ca un fel de diagramă-arbore ca în figura de mai jos. În stânga, selectat în roşu este dosarul (folder) (Windows). Sub el se află sub-dosarele aferente Windows. În dreapta sunt doar sub-dosarele.
A window opens with a sort of diagram like a tree as in the example below. The red selection to the left-side indicates the folder (Windows). Under the folder Windows there are the sub-folders related to this folder. To the right-side there are only the sub-folders.
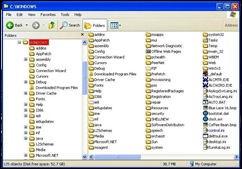
Hard drive este o unitate de stocare permanentă. Se numeşte permanentă pentru că, diferit de RAM, datele rămân pe această unitate, chiar dacă închideţi calculatorul. Totuşi, se mai întâmplă ca acest hard drive să se strice. De aceea, trebuie întotdeauna să vă faceţi copii de siguranţă pentru datele importante. Această acţiune de numeşte back up. Interiorul unui hard drive este arătat mai jos.
The hard drive is a permanent storage device. It's called permanent because, unlike RAM, the data remains on the hard drive even if your computer is turned off. However, hard drives will eventually fail. That's why it's so important that you make copies of your important data. This is called back up. The inside hard drive is shown below.

IMPRIMANTA MULTIFUNCŢIONALĂ = FAX + SCANNER + COPIATOR
MULTI-FUNCTIONAL PRINTER = FAX MACHINE + SCANNER + PRINTER/COPIER
 =
=  +
+  +
+ 
Există sute de modele de imprimante în prezent. Numai dacă nu aveţi nevoie de dispozitive separate, fax, scanner şi copiator, vă recomand o imprimantă multifuncţională.
There are literally hundreds of printers available today. Unless you have a compelling need for a separate printer, fax machine, scanner and photocopier, I recommend one of the fine multi-function printers available.
TASTATURA = MAŞINA DE SCRIS
KEYBOARD = TYPEWRITER
 =
= 
Tastatura în sine nu s-a schimbat în ultimii 100 de ani. Dacă v-aţi descurcat cu o maşină de scris, vă descurcaţi şi cu tastatura de la calculator.
Basic keyboard layouts haven't really changed in the last 100 years. If you "hunt-and-pecked" on a typewriter, then you'll "hunt-and-peck" on a computer keyboard.
MODEMUL = TELEFONUL
MODEM = TELEPHONE
 =
= 
Cuvântul modem vine de la Modulator-Demodulator. Dispozitivul permite calculatorului să se conecteze la un alt calculator printr-o linie de telefon normală. De obicei nu puteţi folosi telefonul când calculatorul foloseşte linia telefonică (dial-up). Multă lume încă mai foloseşte conexiunea la Internet printr-un modem dial up deşi nu recomand această metodă. Majoritatea utilizatorilor accesează Internet prin cablu (high-speed broadband connection) sau prin Digital Subscriber Line (DSL). Cu acest tip de legătură vă puteţi bucura de toate facilităţile Internet. Serviciile DSL şi modem prin cablu sunt accesibile astăzi la preţuri extrem de competitive cu serviciul dial-up. Alte tipuri de modem-uri moderne:
Modem stands for Modulator-Demodulator. A modem allows your computer to connect to another computer using the normal telephone line. Usually, you can not use the telephone when the computer is using the line (dial-up). Many people still connect to the Internet home through a modem using dial-up although this is not recommended. More and more people are now accessing the Internet via a high-speed broadband connection such as a cable modem or a Digital Subscriber Line (DSL). A broadband connection is necessary to fully enjoy all of the multimedia features available on the Internet. DSL and cable modem service is available today at prices that are extremely competitive with dial-up service. Other examples of modern modems:




































